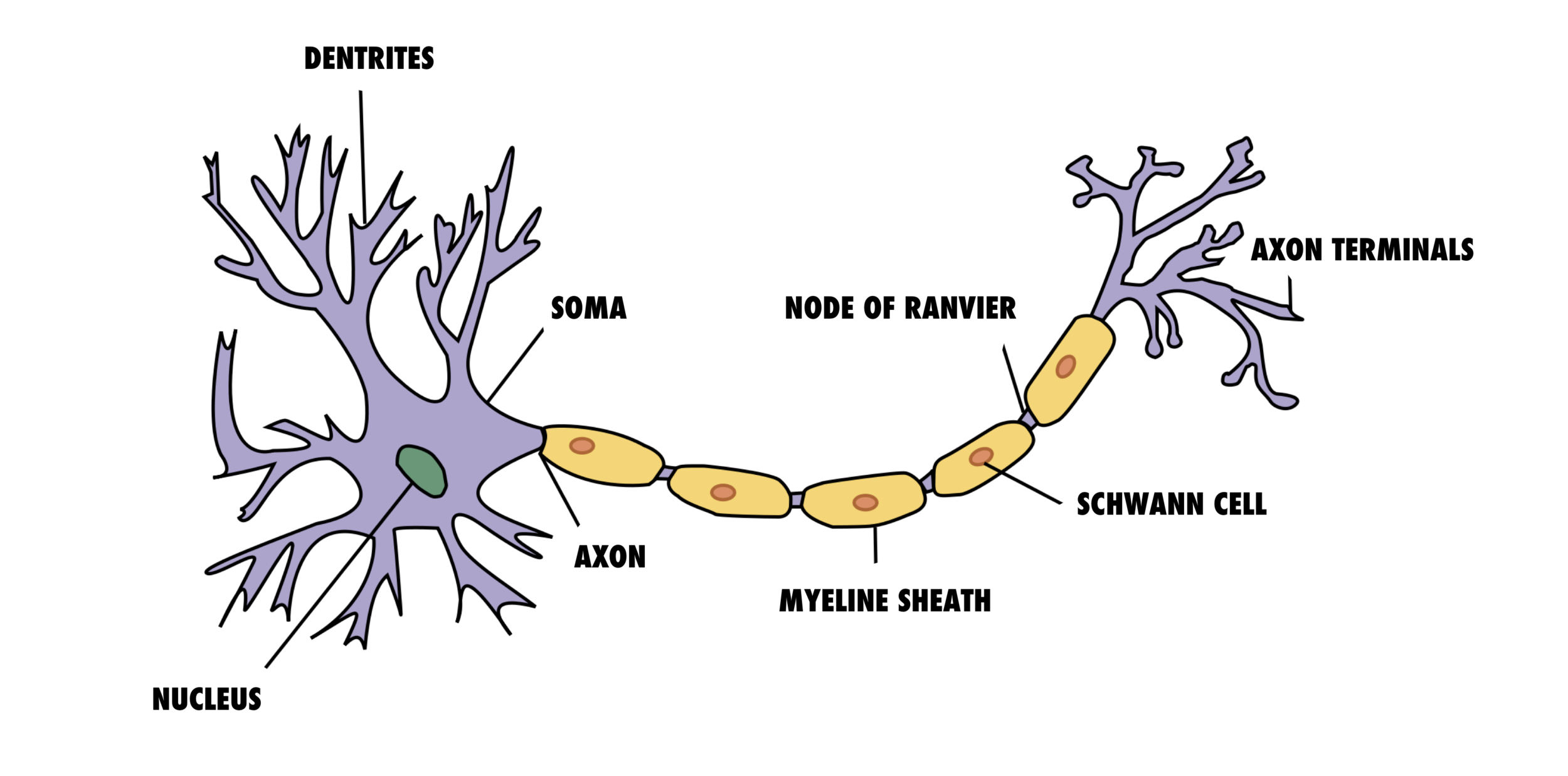
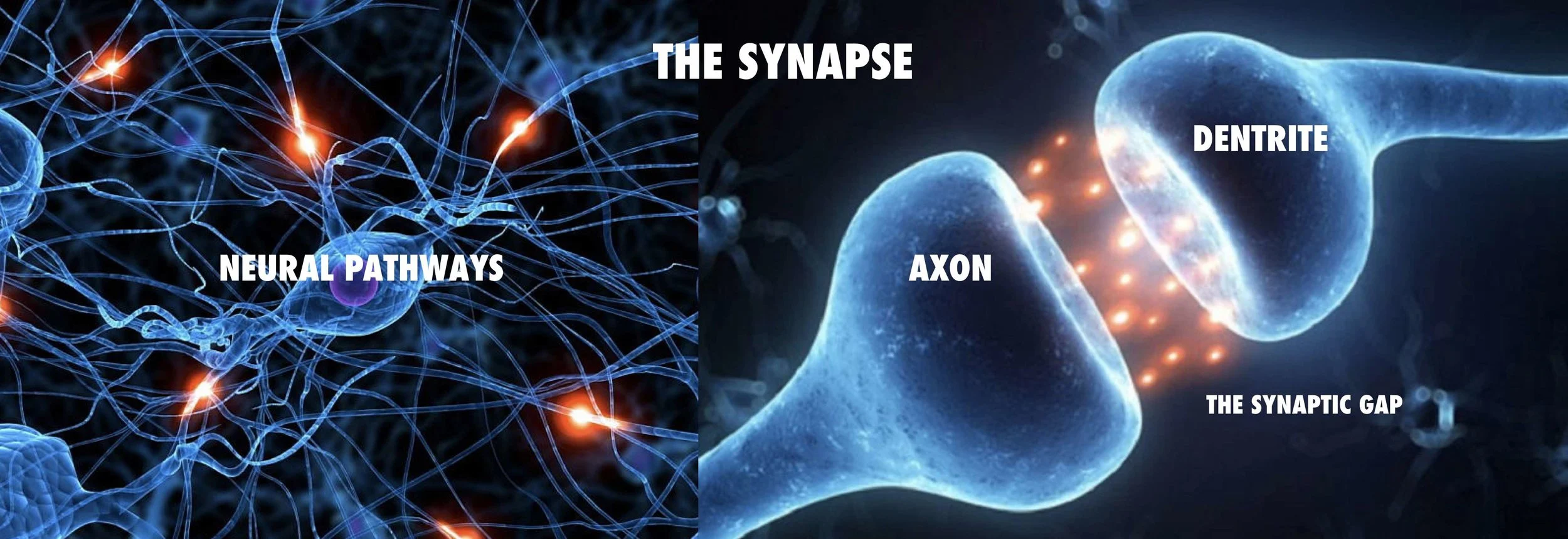
It's desirable to arrange for overachievement by setting realistic visual constructs. This will reward the brain + change neural pathways faster.
Getting Technical:
The frontal lobe – this is located right behind our foreheads. It's this section of the brain that's responsible (among many other actions) for higher-level thinking skills. It's where calculations are processed, decisions are made, and critical thinking tasks are harnessed.
The temporal lobes – these are located on either side of our head, just above the ears and these bits of our brain hold our memory.
The parietal lobes - this is the part that's running along the top of the head, on both the right and left sides, these structures provide the body the feedback for pain, pressure, and touch.
The occipital lobe - this bit is to be found at the back of the head. It occupies 20% of the brain’s overall capacity. This bit is responsible for vision and the ability to visualize scenes. Often these can be scenes never actually witnessed before.
The occipital lobe, among others, is highly engaged when a child reads a story in which there are no pictures, only words to foster the imagination of the book’s events.
Imagine seeing a dozen pictures flash by in a fraction of a second. You might think it would be impossible to identify any images you see for such a short time. However, a team of neuroscientists from MIT has found that the human brain can process entire images that the eye sees for as little as 13 milliseconds — the first evidence of such rapid processing speed.